Renewables
Home Renewables
Renewable Energy and its Benefits


What Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy comes from unlimited, naturally replenished resources, such as the sun, tides, and wind. Renewable energy can be used for electricity generation, space and water heating and cooling, and transportation.
Non-renewable energy, in contrast, comes from finite sources, such as coal, natural gas, and oil.
How Does Renewable Energy Work?
Renewable energy sources, such as biomass, the heat in the earth’s crust, sunlight, water, and wind, are natural resources that can be converted into several types of clean, usable energy:
Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy offers numerous economic, environmental, and social advantages. These include:
- Reduced carbon emissions and air pollution from energy production;
- Enhanced reliability, security, and resilience of the power grid;
- Job creation through the increased production and manufacturing of renewable energy technologies;
- Increased U.S. energy independence;
- Lower energy costs;
- Expanded energy access for remote, coastal, or isolated communities.
Renewable Energy in the United States
Renewable energy generates over 20% of all U.S. electricity, and that percentage continues to grow. The following graphic breaks down the shares of total electricity production in 2022 among the types of renewable power:
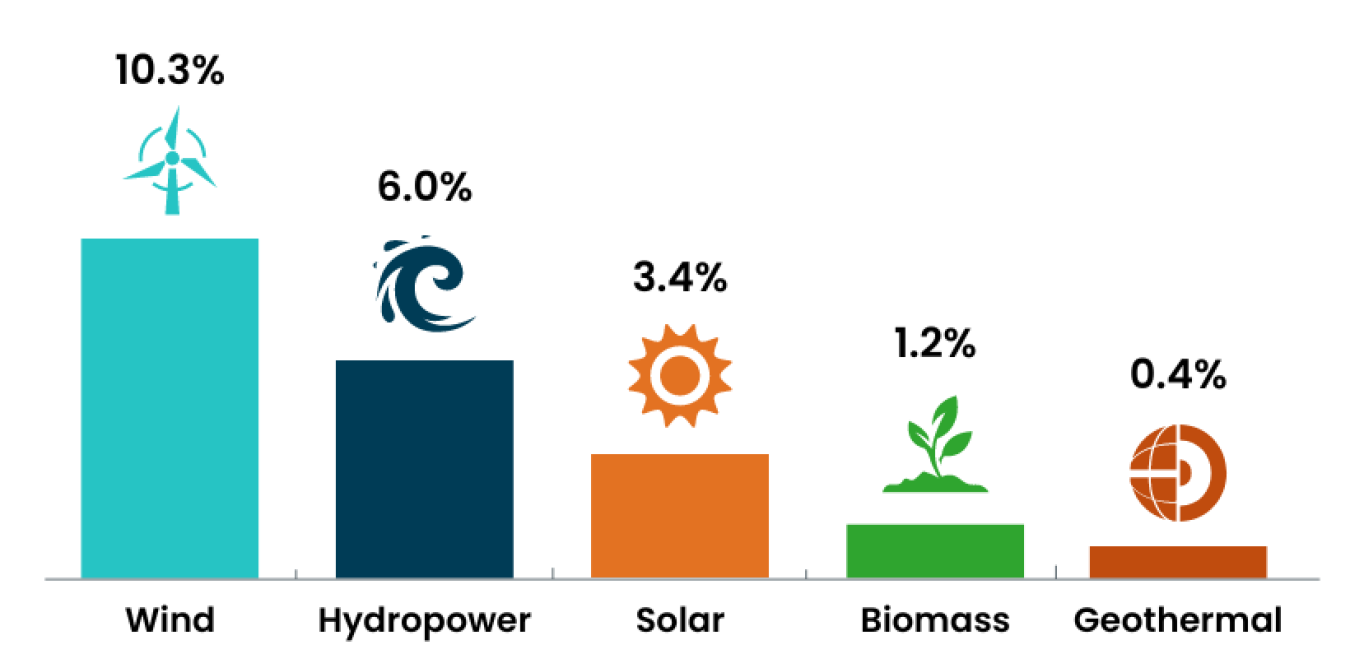
In 2022, annual U.S. renewable energy generation surpassed coal for the first time in history. By 2025, domestic solar energy generation is expected to increase by 75%, and wind by 11%.
The United States is a resource-rich country with enough renewable energy resources to generate more than 100 times the amount of electricity Americans use each year.
Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) has three core divisions: Renewable Energy, Sustainable Transportation and Fuels, and Buildings and Industry. The Renewable Energy pillar comprises four technology offices:
Advancing Renewable Energy in the United States
EERE offers funding for renewable energy research and development, as well as programs that support the sitting of renewable energy, connection of renewable energy to the grid of renewable energy to the grid, and community-led energy projects.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s 17 natural laboratories conduct research and help bring renewable energy technologies to market.
Renewable Energy at Home
Homeowners and renters can use clean energy at home by buying green power, installing renewable energy systems to generate electricity, or using renewable resources for water and space heating and cooling.
Before installing a renewable energy system, it’s important to reduce your energy consumption and improve your home’s energy efficiency.
Visit Energy Saver to learn more about the use of renewable energy at home.
You may be eligible for federal and state tax credits if you install a renewable energy system in your home.
